Desert
Tropical Desert-
I. Description
~Environment of extremes (very hot & very dry)
~The latitude and longitude of the desert is 27.7 degrees N, 8.1 degrees W
~Deserts cover 33% of the earths surface
~Location of desert include: Coastal Chile and Peru
Southern Argentina
Southwest Africa
North Africa
Arabia and Iran
Pakistan and Western India
Baja California and interior Mexico
~Why is named the Tropical Desert?
- Has the highest percentage of sunshine of any climate
- Has the highest daytime temperature of any climate
- The mean annual temperature is 64.4 degrees F
~Plant life-
- Ground hugging shrubs
- Short woody trees
- Cactus
~Animal life-
- Nocturnal carnivores
- Burrowers
- Kangaroo rats
- Insects and reptiles
- Birds
II. Climate
~The Climate of the Tropical Desert is an "arid" climate
~The average rainfall is 25 cm. annually
~The precipitation of the desert is irregular and unreliable
~All water sources are far away and all rain falls in one downfall
~Evaporation is caused by a drop of relative humidity to 10% or less
Temperature
~Average temperature not reach below 64.4 degrees Fahrenheit

III. Biomass and Productivity
- Biomass- the total dry weight of all organic matter in plants and animals in an ecosystem
- Productivity- the rate at which radiant energy is used by producers to form organic substances as food for consumers
~Out of all the biomes the desert is the least productive
~Its net productivity is less than two hundred kilocalories per square meter every year compared to up to 9000 kilocalories per square meter in the other biomes.
~In relation to the productivity, the desert has a low biomass. Because of the scarcity of water, the desert has a lack of biodiversity resulting in a low biomass.
IV. Threats to the Biome
~Development by humans (cities such as Phoenix, Tucson, and Las Vegas are examples)
~Grazing: High levels of grazing can destroy or alter native plant communities, and the grazing animals can trample and kill a variety of desert plants and animals
~Irrigation: If water is not supplied in enough abundance to flow off the land and carry away salts then those salts will build up, leading to salinization of the soil. Salt levels may become too high to support plants.
~Off-road vehicle use: May kill/crush plants while driving, or disrupt soil leading to wind erosion.
~Global Warming: Will a slight temperature rise change anything in an already-hot desert? Yes, even a small change in temperature or precipitation can impact the desert greatly.

V. Animal and Adaptation
Example: the Desert Spiny Lizard.
- well camouflaged to sneak up on prey
- mainly stay in the shade since conditions are so hot

VI. Plant and Adaptation
Desert plants must adapt to the dry conditions.
Example: the Prickly Pear.
- Development of defense structures: Reduced leaves take on the form of spines
- Coating the plant with a thick waxy cuticle: Water loss is reduced
- Water storage in the stem: Critical for survival in the heat

Cold Desert -
I. Description
~Cold deserts are extremely similar to tropical deserts except for the fact that they have more snowfall than rainfall
~The latitude and longitude of the cold deserts are from 15 degrees S - 60 degrees S and 70 degrees W - 80 degrees W
~The majority of rainfall occurs in the winter and occasionally in the short summer
~Antarctica is the world's largest desert
~Locations of the cold desert include: Antarctica
Central Asia
Greenland

~Plant life-
- Different types of grasses
- Arctic Moss
- Flowers: Pasque Flower
- Arctic Willow
~Animal Life-
- Moose
- Arctic Fox
- Polar Bears
- Long- eared jackrabbit
II.Climate
~Like the tropical desert the cold desert experiences a high percentage of sun through out the year and also strong winds.
~The average temperature of cold deserts is between 21-26 degrees C
~ The dry air of the cold deserts do not hold much water vapor and makes rainfall almost impossible.
~During the winter the temperature can get down to -2 degrees C
~The average precipitation fall in the cold desert is 15-26 cm
~Unlike the hot desert the cold deserts precipitation includes snow

III.Biomass and Productivity
~ The cold desert is slightly more productive than the tropical desert because of the snow that moistens the soil and provides a source of water.
~ The cold desert has a net primary productivity of 600 kilocalories per square meter every year. Because of the barren nature of this biome, productivity and biodiversity are limited.
~Since biodiversity is limited, so is biomass. The cold desert is also the lowest of the biomes on the pyramid of biomass (below).
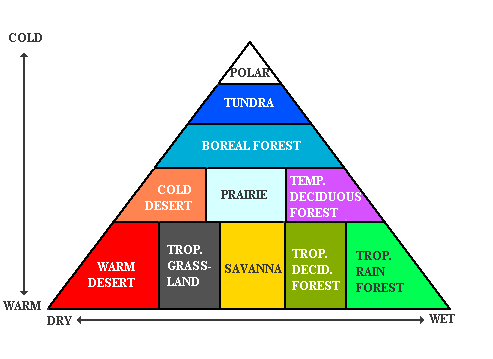
IV. Threats to the Biome
~ The major threat to the cold desert biome is the elevation of airbourne pollutants such as DDT and PCB's.
~ The human threat of gas and oil development also threatens the cold desert biome. For many years, humans have been pushing to use the polars as sources of oil, but, so far, it has been untouched.
~ The cold desert is also threatened by global warming. As the earth heats, the permafrost melts and the ecosystem therefore collapses.
V. Animals and Adaptations
Example: Polar Bear

~ The polar bear's white coat is filled with water repellant hairs and a dense undercoat that covers their feet.
~Polar bears have short, thickly covered snouts and ears to retain heat from the environment.
~ Polar bears also have extremely sensitive noses that can sense things up to 20 miles away and 1 foot underneath the ice.
VI. Plant and adaptation
Example: Saxifrage

~ Saxifrage thrives in the desert biome by growing roots deep into the soil where the heat can be absorbed to stay alive.
~ It is also protected in the winter by a blanket of snow that limits exposure to cold temperatures and strong winds.
Comments (0)
You don't have permission to comment on this page.