http://www.slideshare.net/fozzie/temperate-deciduous-forest-presentation
Location and General Information:
- Deciduous means "falling off or out at a certain season." Thus, the leaves fall off the trees when the winters come, but grow back during the spring season.
- Deciduous forests are located in the temperate zone above tropical forests and below coniferous forests.
- Found in the eastern half of North America, middle of Europe, Asia, and South America.
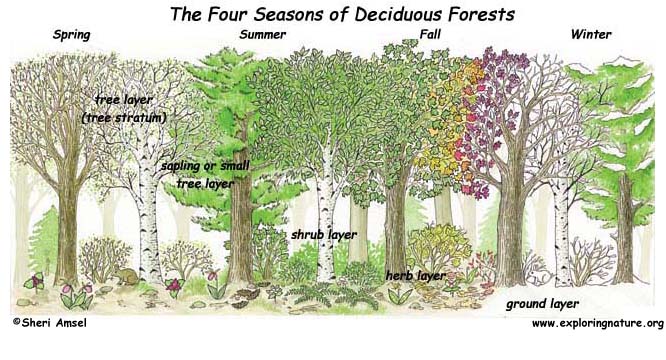
The deciduous forest contains five zones. The first zone is the Tree Stratum zone. This zone contains such trees as oak, beech, maple, chestnut, hickory, elm, basswood, linden walnut, and sweet gum trees. The height of these trees range between 60 and 100 feet. The second zone is the Small Tree and Sapling zone. This zone has young, short trees. The third zone is the Shrub zone. Shrubs found in this zone include mountain laurel, rhododendrons, azaleas, and huckleberries. The fourth zone is the Herb zone. Short plants such as herbal plants are found in this zone. Last, but not least, the fifth zone is called the Ground zone. Lichens, club mosses, and true mosses can be found in this zone.
Climate:
- The average annual temperature is 50 degrees Farenheit.
- The average amount of rainfall is 30-60 inches per year.
- Four seasons:
-Spring: warm and breezy
-Summer: hot and humid, begins in early June and ends in late August, average temperature is 70 degrees Farenheit, about 18 inches of rain
-Autumn: cool and breezy, leaves begin to change color on the trees
-Winter: cold and frosty, trees lose their leaves, average temp. is below freezing, about 14 inches of rain
Most Deciduous Forests are located by an ocean. The ocean and wind affect temperature and climate change.
Biomass and Productivity:
- Contains many tree species within a small area.
- Biomass is relatively high compared to other vegetation communities.
- Most of the biomass appears below ground in the root systems of plants and as partially decomposed plant detritus

This biome contains fertile soil, which has led to the clearing of the forests for agricultural use. This is one of the reasons why there are not a lot of original deciduous forests left in the world. Almost all of the forests in North America are second growth forests, meaning a major disturbance has destroyed the original deciduous forest. However, with some soil or sediment still present, vegetation can germinate and plants can re-grow. In Europe, there are only a few species of original trees left. China has been clearing the natural trees for at least 4,000 years and most of the forests are man-made.
Animals:
Most animals in the deciduous forest are nut and acorn feeders or omnivores. Specific animals include deer, gray squirrels, mice, raccoons, salamanders, snakes, robins, frogs, and mosquitoes.

Animal Adaptations:
- Hibernate in the winter and live off the land in the other three seasons. Animals that hibernate protect themselves against the cold and reduce their need for food. A hibernating animal's body temperature is lower than normal and its heartbeat and breathing slow down greatly. An animal in this state needs little energy to stay alive and can live off fat stored in its body.
- Have adapted to the land by trying the plants in the forest to see if they are good to eat for a sufficient supply of food
- Use the trees for shelter, food, and water sources
- Many animals are camouflaged to look like the ground in order to avoid predators
- Some animals store large supplies of food, such as seeds and nuts, in the ground, under fallen leaves, or in tree hollows for use during the winter when food is scarce. Cold temperatures help prevent the decomposition of nuts and seeds.
Specific Animal Adaptations:
The white-tailed deer is one specific animals that has adapted over time. The deer eats green plants in the summer. However, when the leaves fall in the winter, it eats nuts, acorns, and twigs to survive. In order to keep warm during the winter, the deer form herds. These animals have a protective coloring that allow them to hide in the undergrowth. In order to avoid predators, such as humans and other animals, they make snorting sounds and stamp their hooves to alert other deer of danger. While running, a deer will often raise its tail so other deer will have a guide to follow away from danger. Over time, the deer has developed good eyesight and hearing to avoid predators and seek protection.


The European Red Squirrel is another common animal of the deciduous forest. These organisms have strong teeth to open pinecones and seeds as well as four toes with long, sharp claws on each foot to help them grab bark when climbing trees. They can support their weight when climbing a tree due to their long bushy tail, adapted over time for balance. To help the red squirrel keep safe in its environment, it climbs quickly. When the squirrel is mad, it will wave it tail back and forth like a flag. They are important to the environment because they disperse seeds. However, many are endangered because they can't compete with the more adaptable gray squirrel. Also, many are trapped for their fur and their habitats are being destroyed.


Plants:
Most plants are broad-leaf deciduous trees which turn colors of red and gold in the fall and lose their leaves in the winter. Examples of such trees are oak, hickory, maple, poplar, and sycamore. Evergreen trees are also common.
The decidous forest contains layers of plants, which depend upon the climate, soil, and age of the forest. These layers of plants fall under the five zones talked about under the first subsection. The forest canopy (tree stratum zone) contains the tallest trees which are highly dependent upon sunlight for photosynthesis. The understory (small tree zone) contains trees that are more shade tolerant. The shrub layer (shrub zone) contain many shrubs which grow food for the animals. The herb layer (herb zone) carpets the forest floor and is made up of wildflowers, mosses, and ferns. Last, the ground (ground zone) contains fallen leaves, twigs, and dried up plants which decompose and add nutrients to the topsoil.


Plant Adaptations:
- Grow at an angle leaning toward the sun in order to maintain the process of photosynthesis. Such penetration of sunlight supports a richer diversity of plant life at the ground level.
- Soak up nutrients in the ground, which animals consume by eating the plants.
- The low rate of decomposition allows the accumulation of a thick layer of slowly decaying leaf litter to provide nutrients

Specific Plant Adaptations:
- Wildflowers grow on the forest floor early in the spring before trees "leaf-out" and shade the floor.
- Deciduous trees have thin, broad, light-weight leaves that capture a lot of sunlight to make food for the tree in warm weather. In cold weather, the leaves lose too much water and can be weighed down by snow, so the leaves fall in the winter to prevent the tree from dying.
- Most trees have thick barks to protect against the cold winters.


Threats to the Deciduous Forest:
- Human intervention: Many of the forests have been converted into farms or towns, thus destroying the habitats of many animals
- Poachers hunt the animals for fur, food, or recreational activity
- Acid rain cause by industrial and vehicular emissions. The acid rain damages tree leaves, causes trees to produce fewer and smaller seeds, and reduces resistance to diseases.
- Spread of invasive species that compete for space and food
- Many of the forests are cleared and replaced with tree plantations consisting of single tree species. These new trees are harvested as Christmas trees, timber, or wood converted into the paper we use today.
- Mining damages the land to the extent that forests cannot re-grow on the depleted soils.
Comments (0)
You don't have permission to comment on this page.